栈本质上是线性表,而且是操作受限的线性表。
栈的概念
栈,是一种后进先出(LIFO, last in first out)的线性数据结构。与一般线性表(数组、链表)不同,栈是一种操作受限的线性表,只允许在栈的一端进行出栈(pop)和入栈(push)操作。
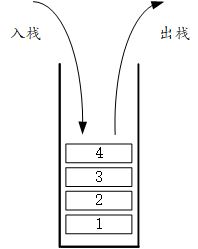
把线性表看成上图中的桶,只允许在表的一端进行入栈和出栈操作,这个桶就是栈。
如上图所示,以1、2、3、4的顺序依次将数据推入栈中,最先进去的1在栈的最底部,而最后进去的4则在栈的最上方。由于只能在栈的顶部出入,所以如果此时出栈,那么最后进去的4反而会成为出栈的元素。
实现
这里使用C++语言示范,栈中存储的数据类型为int
首先定义一个容量为maxSize的数组,这里设置为100。
1
2
3
| int maxSize = 100;
int top = -1;
int* stack = new int[maxSize];
|
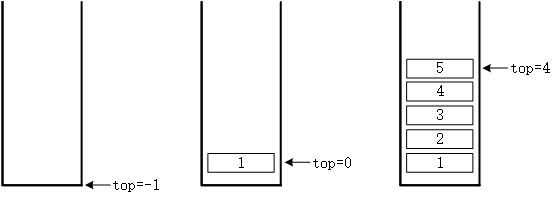
top是一个int类型的值,称之为栈中的头指针或者栈顶。top永远指向当前栈中存储的数据的顶部,在初始化时,栈中是空的,所以我们将top值设为1 。可以发现,当top = -1时表示空栈,也就是栈里没有数据,当top >= 0时,即表示当前栈顶的元素为stack[top]。
1
2
| top++;
stack[top] = value;
|
入栈时先将top加1,然后设置栈顶的值。当然,实际使用时要注意检查top指针是否越界。
取栈顶元素时也很简单
top指向的也就是栈顶的值
出栈时,首先取到栈顶的值,再将top减1即可。
1
2
| int value = stack[top];
top--;
|
value即是出栈前,栈顶的元素。出栈时我们并不需要手动的再将原先的元素在数组中的数据清空,只需要简单的修改top指针指向的位置,在下一次入栈时原先的数据将会被直接覆盖。同样的道理,清空整个栈也只需要将top设为-1就可以了。
总结
栈是程序设计中非常常用的一个数据结构,虽然本质上是线性表,但是限制操作后就可以看成是一种具有后进先出特性的线性表,看似有限的操作空间,但是在使用上却更为简遍。其实这就是一种封装,将数组或者链表封装成栈之后,不需要使用者去人为的管理维护这个数组或者是链表,只需要简单的调用push()/pop(),使代码更简洁,也减少了出错的可能性。
完整代码
在细节上有一些小问题,所以仅供参考。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
template <class Type>
class ArrayStack {
private:
int top;
int maxSize;
Type* date;
public:
ArrayStack();
ArrayStack(int max);
~ArrayStack();
bool push(Type d);
Type pop();
Type getTop();
int getSize();
bool isEmpty();
void setEmpty();
};
template <class Type>
ArrayStack<Type>::ArrayStack() {
top = -1;
maxSize = 100;
date = new Type[maxSize];
}
template <class Type>
ArrayStack<Type>::ArrayStack(int max) {
top = -1;
maxSize = max;
date = new Type[maxSize];
}
template <class Type>
ArrayStack<Type>::~ArrayStack() {
top = -1;
delete date;
date = nullptr;
}
template <class Type>
bool ArrayStack<Type>::push(Type d) {
if (top + 1 == maxSize) {
return false;
}
top++;
date[top] = d;
return true;
}
template <class Type>
Type ArrayStack<Type>::pop() {
if (top == -1) {
return false;
}
Type temp = date[top];
top--;
return temp;
}
template <class Type>
Type ArrayStack<Type>::getTop() {
if (top == -1) {
return false;
}
Type temp = date[top];
return temp;
}
template <class Type>
int ArrayStack<Type>::getSize() {
return top + 1;
}
template <class Type>
bool ArrayStack<Type>::isEmpty() {
return (top == -1 ? true : false);
}
template <class Type>
void ArrayStack<Type>::setEmpty() {
top = -1;
}
|

